AC, DC and HPC charging stations
Electric mobility is changing driving habits and brings with it new questions about charging electric cars: where can I charge, how long does it take, which charging station should I choose?
To answer these questions, it is useful to start with the three main categories into which charging stations are divided, based on the type of current they use and the power delivered: AC (alternating current), DC (direct current), and HPC (High Power Charging).
What do AC, DC, and HPC mean?
Alternating current (AC) is the type of electricity we receive from the power grid and use daily at home to supply electrical and electronic devices. In this type of electric flow, the direction of electrons changes periodically, making it easier to transform voltage and transport energy over long distances with lower losses.
Direct current (DC), on the other hand, is a constant, unidirectional electric flow in which electrons always move in the same direction. It is ideal for batteries and accumulators: we find it in batteries, smartphones, laptops, and electric car batteries. The latter, in fact, can store energy only as direct current. For this reason, the electric charging process changes depending on the type of current used by the charging station:
AC charging stations supply alternating current, which the car must then convert into direct current through an onboard converter.
DC charging stations (and HPC) supply direct current directly. The conversion already takes place inside the charging station, and the energy reaches the battery ready for use.
What are the differences between AC, DC, and HPC charging stations?
In addition to the type of current, charging stations differ in characteristics mainly related to the power delivered (and therefore charging speed), costs, installation location, and the type of connector used.
Power and charging speed
For clear communication with customers, Enel X Way uses the following classifications based on power:
| Category | Type of current | Power delivered | Typical charging speed |
|---|---|---|---|
|
AC |
Alternating |
Up to 22 kW |
Slow/accelerated (hours) |
|
DC |
Direct |
Up to 99 kW |
Fast (tens of minutes) |
|
HPC |
Direct |
From 100 kW and above |
Ultra-fast (a few minutes) |
Due to the different power delivered, AC charging stations require longer times to charge a battery, which is why they are ideal when the car can remain parked for several hours. DC charging stations and, even more so, HPC stations are much faster and allow the battery to be charged in a short time, making them the ideal solution for long journeys and quick stops.
Installation, costs, and infrastructure
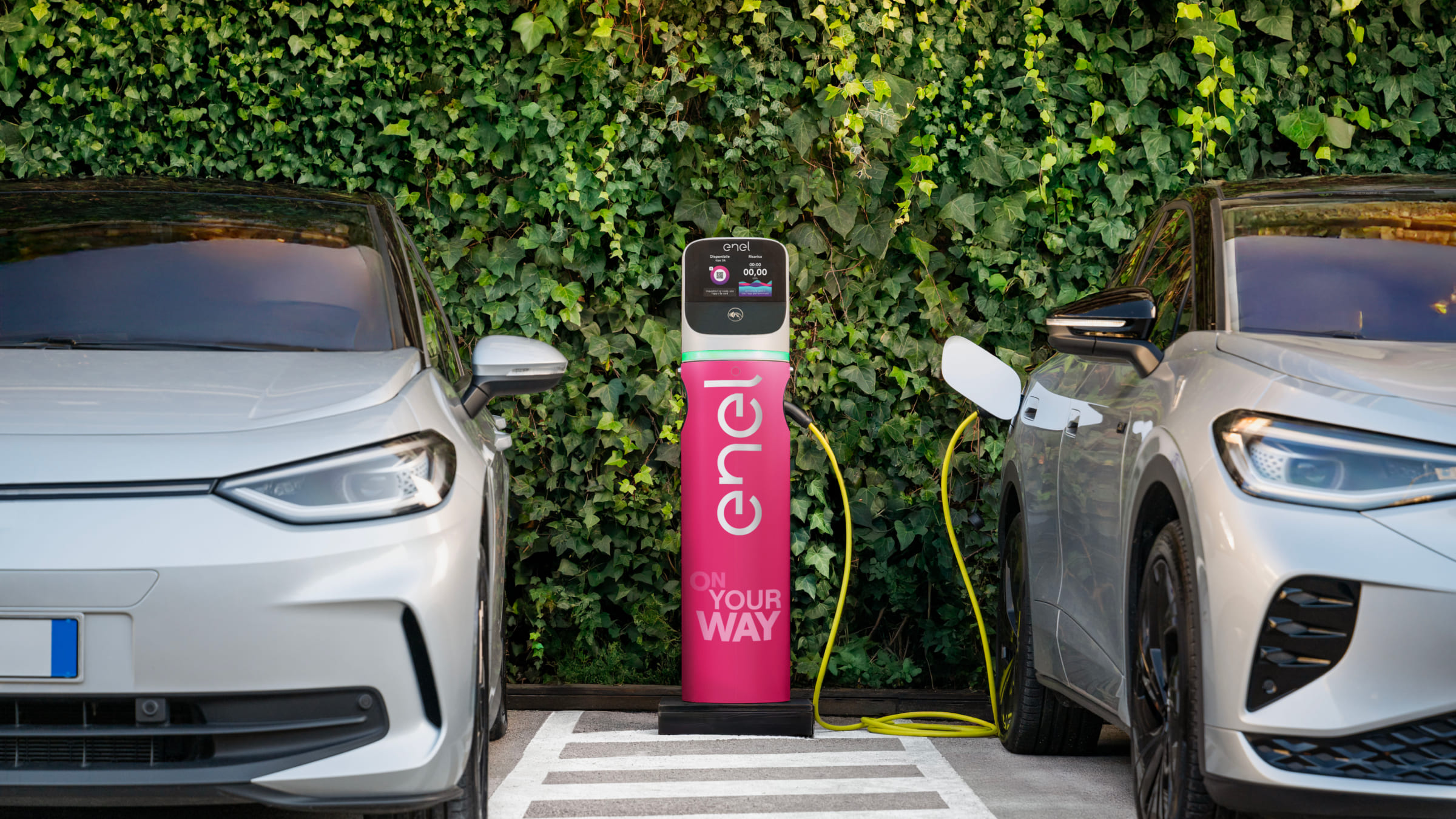
In terms of distribution, AC charging stations (up to 22 kW) are more widely available in urban and residential areas, including private homes, apartment buildings, company parking lots, supermarkets, and public spaces.
By contrast, DC charging stations (up to 99 kW) and HPC stations (from 100 kW and above) are strategically located along highways, at service stations, or in areas with high vehicle traffic where fast charging is required.
From a technical perspective, AC charging stations are more accessible thanks to a simple infrastructure connected to the standard power grid and require limited maintenance. DC and HPC charging stations, on the other hand, are more complex, require connections to the medium-voltage power grid and more advanced management systems, which is why they are mainly installed in public or strategic areas.
To view the entire Enel X Way charging network (CPO), consult our map. Alternatively, to access the complete map of all available charging points, you can download the Enel X Way app, available for Android and Apple operating systems.



AC vs DC/HPC: which charging station should you choose?
There is no one-size-fits-all answer: AC, DC, and HPC charging stations are not in competition with each other, but are three complementary solutions. The choice therefore depends on your needs and on how, where, and how often you use your electric car.
AC charging is the most common and widespread option and is ideal for those who have longer time available or can schedule charging in advance. It is the perfect solution for charging your car at home overnight, at the office, or in public parking areas.
It is less stressful for the battery and more cost-effective in terms of both energy and infrastructure. It does not require high power levels and can be easily installed even in domestic or condominium settings.
DC and HPC charging are the right choice when speed is a priority. They are designed for those who cannot afford long waiting times or need to recharge in a short time. They are particularly suitable during long journeys, on highways or in rest areas, for company fleets or commercial vehicles, or in high-turnover contexts.
With a DC or HPC charging station, the battery can be recharged in less than an hour, but costs are higher and more complex infrastructure is required. For this reason, they are almost always found in public or strategic locations.