What is a condensing boiler and how does it work?
What is a condensing boiler and how does it work?
A condensing boiler is a modern heating and domestic hot water production technology, an evolution of the traditional gas boiler, which optimises energy performance, reduces pollutant emissions, and lowers the costs of your bill.
So let's see how a condensing boiler works.
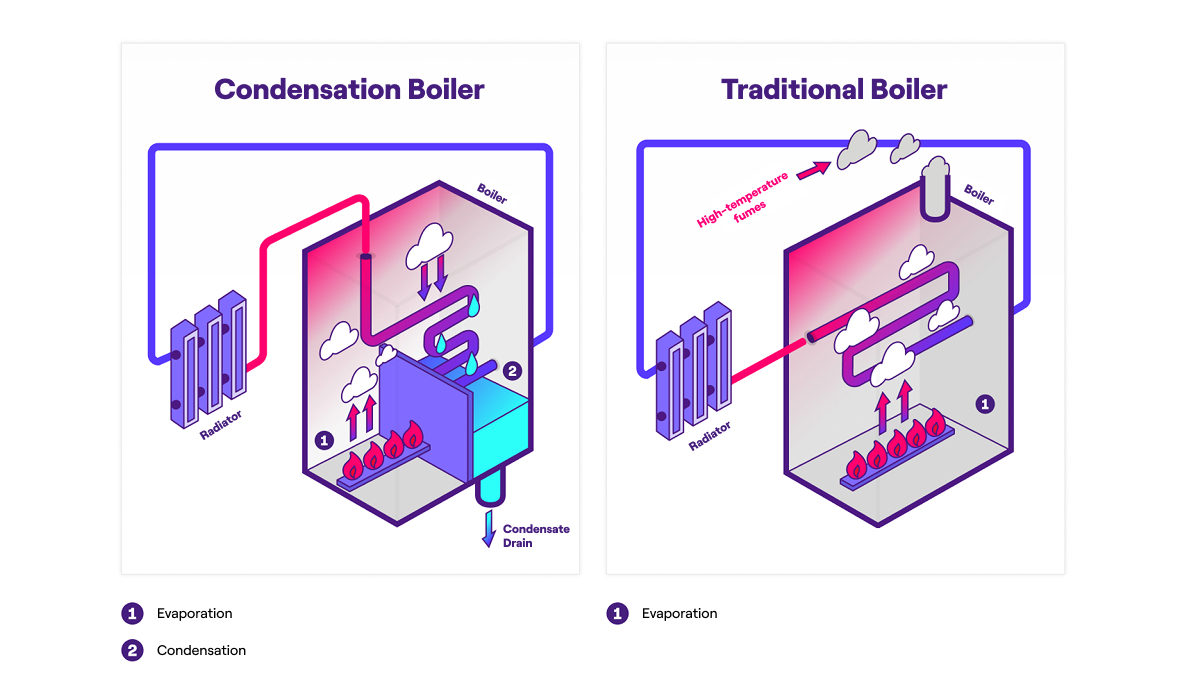
Through combustion, the gas develops heat, which is transferred to the water in the heating system via an exchanger. Water vapour is also produced during this process, due to the natural moisture in the air supplied to fuel combustion, which is normally expelled along with the flue gases via the chimney. In condensing boilers, on the other hand, the flue gases are cooled until the steam present in them condenses, thus giving up its latent heat to the water entering the boiler, preheating it. This technology therefore avoids dispersion of residual heat downstream of combustion and makes better use of the thermal energy produced, reducing gas consumption and therefore, your bills.
Compared to conventional boilers, the operation of a condensing boiler requires the presence of a condensate drain, which, being acidic, must be piped to a sewer.
How much can you save with a condensing boiler?
In a condensing boiler, water is heated by the heat of combustion, as in conventional boilers, but the dispersion of residual thermal energy contained in the high-temperature flue gases is avoided.
This recovery of latent heat, which occurs thanks to the condensation process, can cut consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional technology and makes it possible to amortise the cost of a condensing boiler.
Another advantage comes from low pollutant emissions, such as nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide, again thanks to condensing technology.
Another saving factor can be the combination with a smart thermostat, which can optimise the on and off times of the domestic heating system according to household habits.